A 3D window into living cells, no dye required
January 27, 2014
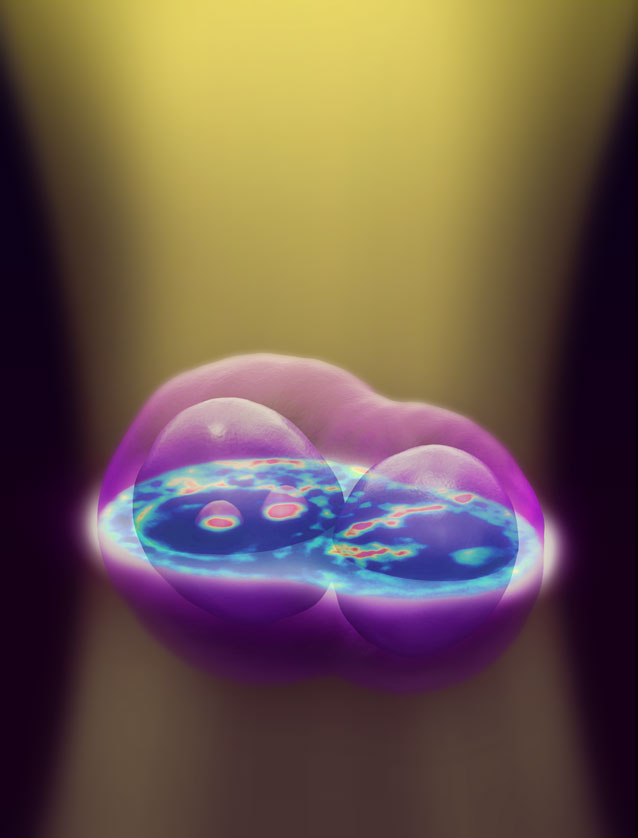
A new 3D imaging technique for live cells uses a conventional microscope to capture image slices throughout the depth of the cell, then computationally renders them into one three-dimensional image. The technique uses no dyes or chemicals, allowing researchers to observe cells in their natural state. (Credit: University of Illinois)
University of Illinois researchers have developed a new imaging technique that needs no dyes or other chemicals, yet renders high-resolution, three-dimensional, quantitative imagery of cells and their internal structures using conventional microscopes and white light.
Called white-light diffraction tomography (WDT), the imaging technique opens a window into the life of a cell without disturbing it and could allow cellular biologists unprecedented insight into cellular processes, drug effects and stem cell differentiation.
The team, led by electrical and computer engineering and bioengineering professor Gabriel Popescu, published their results in the journal Nature Photonics.
“One main focus of imaging cells is trying to understand how they function, or how they respond to treatments, for example, during cancer therapies,” Popescu said. “If you need to add dyes or contrast agents to study them, this preparation affects the cells’ function itself. It interferes with your study. With our technique, we can see processes as they happen and we don’t obstruct their normal behavior.”
Capturing images in different planes
Because it uses white light, WDT can observe cells in their natural state without exposing them to chemicals, ultraviolet radiation, or mechanical forces — the three main methods used in other microscopy techniques. White light also contains a broad spectrum of wavelengths, thus bypassing the interference issues inherent in laser light — speckles, for example.
The 3-D images are a composite of many cross-sectional images, much like an MRI or CT image. The microscope shifts its focus through the depth of the cell, capturing images of various focus planes. Then the computer uses the theoretical model and compiles the images into a coherent three-dimensional rendering.
The greatest potential of WDT, according to the researchers, is the ability to study cells in three dimensions over time. Since the cells are not altered, they can be imaged repeatedly, allowing researchers a glimpse into the dynamics of a cell as it goes about its life — or as it is treated with a new drug.
“As a cell grows we can see the change in all three dimensions,” said Taewoo Kim, a graduate student and first author of the paper. “We can see the dynamics of the cell in 3-D, which hasn’t been done in a quantitative manner. For example, we could see, in the span of a minute or over a cell’s lifetime, how it grows and how the things in the cell move around.”
“With this imaging we can tell at what scale things within the cell are transported randomly and at what scale processes are actually organized and deterministic,” Popescu said. “At first glance, the dynamics looks pretty messy, but then you look at it — we stare at movies for hours and hours — and you realize it all makes sense. Everything is organized perfectly at certain scales. That’s what makes a cell alive. Randomness is just nature’s way to try new things.”
WDT uses a component that adds onto a conventional phase contrast microscope, a common piece of equipment in biology labs, without altering the microscope itself. The researchers used conventional microscopes with the intention of making these new optics principles easily accessible for biologists. The researchers hope that this will allow rapid large-scale adoption of WDT, and Popescu founded a startup company, Phi Optics, to help achieve that goal.
In addition to biological applications, the WDT technique has implications in the broader field of optics as the researchers pushed the boundaries of physics by applying scattering theory to imaging optics.
“The physics behind this technique is another thing we were fascinated about,” Kim said. “Light propagation in general is studied with approximations, but we’re using almost no approximation. In a very condensed form, we can perfectly show how the light changes as it passes through the cell.”
“We started on this problem two years ago, trying to formulate mathematically the sectioning effect observed in spatial light interference light microscopy (SLIM),” said Renjie Zhou, a graduate student and co-first author of the paper. “We came up with equations which eventually described WDT. The final equation is beautiful and the theory opens opportunities for solving other optics problems in a new theoretical language.”
Next, the researchers hope to pursue cross-disciplinary collaborations to explore applications of WDT in biology as well as expansions of the imaging optics demonstrated in WDT. For example, they are using WDT to watch stem cells as they differentiate in hopes of better understanding how they turn into different cell types. Since stem cells are so sensitive, only a chemical-free, non-invasive, white-light technique such as WDT could be used to study them without adverse effects.
The National Science Foundation supported this work.
Abstract of Nature Photonics paper
We present a technique called white-light diffraction tomography (WDT) for imaging microscopic transparent objects such as live unlabelled cells. The approach extends diffraction tomography to white-light illumination and imaging rather than scattering plane measurements. Our experiments were performed using a conventional phase contrast microscope upgraded with a module to measure quantitative phase images. The axial dimension of the object was reconstructed by scanning the focus through the object and acquiring a stack of phase-resolved images. We reconstructed the three-dimensional structures of live, unlabelled, red blood cells and compared the results with confocal and scanning electron microscopy images. The 350 nm transverse and 900 nm axial resolution achieved reveals subcellular structures at high resolution in Escherichia coli cells. The results establish WDT as a means for measuring three-dimensional subcellular structures in a non-invasive and label-free manner.