A batteryless cardiac pacemaker based on self-winding wristwatch
September 2, 2014
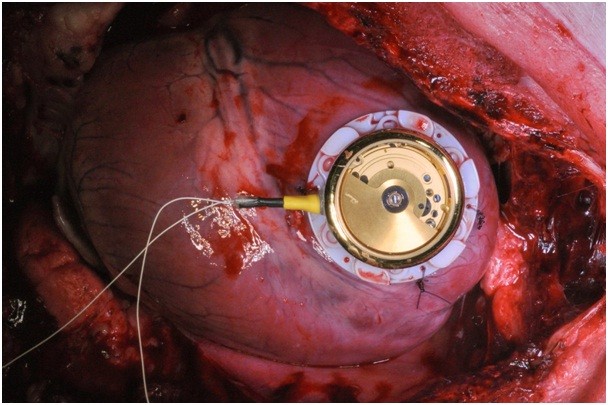
The energy harvesting device is sutured directly onto the myocardium (credit: European Society of Cardiology)
A new batteryless cardiac pacemaker controlled by a self-winding wristwatch mechanism that is powered by heart motion has been developed by researchers in the Cardiovascular Engineering Group at ARTORG, University of Bern, Switzerland.
The device was presented at European Society of Cardiology (ESC) Congress 2014 by Adrian Zurbuchen a PhD candidate.
“Batteries are a limiting factor in today’s medical implants,” he said. “Once they reach a critically low energy level, physicians [are] forced to replace a correctly functioning medical device in a surgical intervention. This is an unpleasant scenario which increases costs and the risk of complications for patients.”
Four years ago Professor Rolf Vogel, a cardiologist and engineer at the University of Bern, had the idea of using a self-winding wristwatch mechanism to harvest the energy of heart motion. “The heart seems to be a very promising energy source because its contractions are repetitive and present for 24 hours a day, 7 days a week,” said Zurbuchen. ” Furthermore the automatic clockwork, invented in the year 1777, has a good reputation as a reliable technology to scavenge energy from motion.”
The researchers’ first prototype is based on a commercially available automatic wristwatch. All unnecessary parts were removed to reduce weight and size. They also developed a custom-made housing with eyelets that allows suturing the device directly onto the myocardium.
How it works
The prototype works the same way it would on a person’s wrist. When it is exposed to an external acceleration, the eccentric mass of the clockwork starts rotating. This rotation progressively winds a mechanical spring. After the spring is fully charged it unwinds and thereby spins an electrical micro-generator.
To test the prototype, the researchers developed an electronic circuit to transform and store the signal. They then connected the system to a custom-made cardiac pacemaker. The system worked in three steps. First, the harvesting prototype acquired energy from the heart. Second, the energy was temporarily stored in the buffer. And finally, the buffered energy was used by the pacemaker to apply minute stimuli to the heart.
The researchers successfully tested the system in in vivo experiments with domestic pigs. The newly developed system allowed them for the first time to perform batteryless overdrive-pacing at 130 beats per minute.
“The next step … is to integrate both the electronic circuit for energy storage and the custom-made pacemaker directly into the harvesting device. This will eliminate the need for leads.
“Our new pacemaker tackles the two major disadvantages of today’s pacemakers. Pacemaker leads are prone to fracture and can pose an imminent threat to the patient. And the lifetime of a pacemaker battery is limited. Our energy harvesting system is located directly on the heart and has the potential to avoid both disadvantages by providing the world with a batteryless and leadless pacemaker.”