Almost 3,000 atoms entangled with a single photon
March 25, 2015
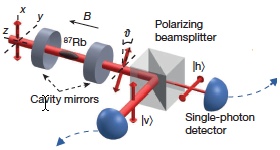
Generating entanglement of 2,910 atoms (credit: Robert McConnell et al./Nature)
Physicists from MIT and the University of Belgrade have developed a new technique that can entangle 2,910 atoms using only a single photon — the largest number of particles that have ever been mutually entangled experimentally (previous record: 100).
The researchers say the technique provides a realistic method to generate large ensembles of entangled atoms, which are key components for realizing more-precise atomic clocks and more powerful computers.
“You can make the argument that a single photon cannot possibly change the state of 3,000 atoms, but this one photon does — it builds up correlations that you didn’t have before,” says Vladan Vuletic, the Lester Wolfe Professor in MIT’s Department of Physics, and the paper’s senior author. “We have basically opened up a new class of entangled states we can make, but there are many more new classes to be explored.”
The entanglement concept was first proposed in a 1935 paper by Albert Einstein, Boris Podolsky and Nathan Rosen: two or more particles may be correlated in such a way that any change to one will simultaneously change the other, no matter how far apart they may be. For instance, if one atom in an entangled pair were somehow made to spin clockwise, the other atom would instantly be known to spin counterclockwise, even though the two may be physically separated by thousands of miles.
The idea was dismissed by Einstein as “”spooky action at a distance,” but in a paper published yesterday (March 24) in Nature Communications, researchers at Griffith University and the University of Tokyo reported measurements that confirm non-local collapse of a particle’s wave function. The scientists used homodyne detectors — which measure wave-like properties — to confirm splitting of a single photon between two laboratories.
Scientists have been searching for ways to entangle large numbers of atoms, which could be the basis for powerful quantum computers and more-precise atomic clocks.
Picking up quantum noise
Scientists have so far been able to entangle large groups of atoms, although most attempts have only generated entanglement between pairs in a group. Only one team has successfully entangled 100 atoms — the largest mutual entanglement to date, and only a small fraction of the whole atomic ensemble.
Now Vuletic and his colleagues have successfully created a mutual entanglement among 2,910 atoms, virtually all the atoms in the 3,100 atoms ensemble, using very weak laser light — down to pulses containing a single photon. The weaker the light, the better, Vuletic says, as it is less likely to disrupt the cloud. “The system remains in a relatively clean quantum state,” he says.
The researchers first cooled a cloud of atoms, then trapped them in a laser trap, and sent a weak laser pulse through the cloud. They then set up a detector to look for a particular photon within the beam. Vuletic reasoned that if a photon has passed through the atom cloud without event, its polarization, or direction of oscillation, would remain the same.
If, however, a photon has interacted with the atoms, its polarization rotates just slightly — a sign that it was affected by quantum “noise” in the ensemble of spinning atoms, with the noise being the difference in the number of atoms spinning clockwise and counterclockwise.
“Every now and then, we observe an outgoing photon whose electric field oscillates in a direction perpendicular to that of the incoming photons,” Vuletic says. “When we detect such a photon, we know that must have been caused by the atomic ensemble, and surprisingly enough, that detection generates a very strongly entangled state of the atoms.”
Vuletic and his colleagues are currently using the single-photon detection technique to build a state-of-the-art atomic clock* that they hope will overcome what’s known as the “standard quantum limit” — a limit to how accurate measurements can be in quantum systems. Vuletic says the group’s current setup may be a step toward developing even more complex entangled states.
“This particular state can improve atomic clocks by a factor of two,” Vuletic says. “We’re striving toward making even more complicated states that can go further.”
This research was supported in part by the National Science Foundation, the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency, and the Air Force Office of Scientific Research.
* Today’s best atomic clocks are based on the natural oscillations within a cloud of trapped atoms. As the atoms oscillate, they act as a pendulum, keeping steady time. A laser beam within the clock, directed through the cloud of atoms, can detect the atoms’ vibrations, which ultimately determine the length of a single second.
The accuracy of atomic clocks improves as more and more atoms oscillate in a cloud. Conventional atomic clocks’ precision is proportional to the square root of the number of atoms: For example, a clock with nine times more atoms would only be three times as accurate. If these same atoms were entangled, a clock’s precision could be directly proportional to the number of atoms — in this case, nine times as accurate. The larger the number of entangled particles, then, the better an atomic clock’s timekeeping.
UPDATE 3/25/2015: Added mention of research confirming the entanglement theory.
Abstract of Entanglement with negative Wigner function of almost 3,000 atoms heralded by one photon
Quantum-mechanically correlated (entangled) states of many particles are of interest in quantum information, quantum computing and quantum metrology. Metrologically useful entangled states of large atomic ensembles have been experimentally realized, but these states display Gaussian spin distribution functions with a non-negative Wigner quasiprobability distribution function. Non- Gaussian entangled states have been produced in small ensembles of ions, and very recently in large atomic ensembles. Here we generate entanglement in a large atomic ensemble via the interaction with a very weak laser pulse; remarkably, the detection of a single photon prepares several thousand atoms in an entangled state. We reconstruct a negative-valued Wigner function—an important hallmark of non-classicality—and verify an entanglement depth (the minimum number of mutually entangled atoms) of 2,910 ± 190 out of 3,100 atoms. Attaining such a negative Wigner function and the mutual entanglement of virtually all atoms is unprecedented for an ensemble containing more than a few particles. Although the achieved purity of the state is slightly below the threshold for entanglement- induced metrological gain, further technical improvement should allow the generation of states that surpass this threshold, and of more complex Schrödinger cat states for quantum metrology and information processing. More generally, our results demonstrate the power of heralded methods for entanglement generation, and illustrate how the information contained in a single photon can drastically alter the quantum state of a large system.