Better than X-rays: a more powerful terahertz imaging system
March 29, 2013
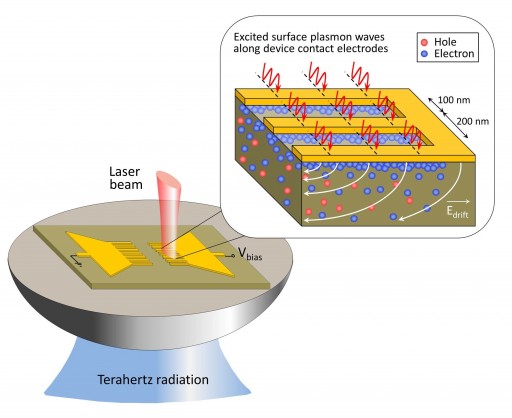
Schematic diagram and operation concept for plasmonic terahertz devices (credit: C.W. Berry et al./University of Michigan)
An electrical engineering research team at the University of Michigan has developed a laser-powered terahertz source and detector system that transmits with 50 times more power and receives with 30 times more sensitivity than existing technologies.
This offers 1,500 times more powerful systems for imaging and sensing applications.
Low-energy terahertz radiation could potentially enable doctors to see deep into tissues without the damaging effects of X-rays, or allow security guards to identify chemicals in a package without opening it.
But it has been difficult for engineers to make powerful enough systems to accomplish these promising applications.
The research team accomplished this by funneling the laser light to specifically selected locations near the device’s electrode that feeds the antenna that transmits and receives the terahertz signal.
Their approach enables light to hitch a ride with free electrons on the surface of the metallic electrodes to form a class of surface waves called surface plasmon waves.
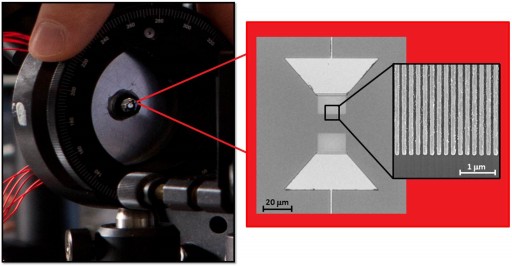
Microscope image of the plasmonic terahertz source/detector prototype and the scanning electron microscope image of the plasmonic electrodes (credit: C.W. Berry et al./University of Michigan)
By coupling the beam of light with surface plasmon waves, the researchers created a funnel to carry light into nanoscale regions near device electrodes. The excited surface plasmon waves carry optical photons where they need to be much faster and much more efficiently, said Mona Jarrahi, U-M assistant professor of electrical engineering and computer science and leader of the project.
“When you want to generate or detect terahertz radiation, you have to convert photons to electron hole pairs and then quickly drift them to the contact electrodes of the device. Any delay in this process will reduce the device efficiency,” Jarrahi said. “We designed a structure so that when photons land, most of them appear to be right next to the contact electrodes.”
According to Jarrahi, the output power of the terahertz sources and the sensitivity of the terahertz detectors can be increased even further by designing optical funnels with tighter focusing capabilities.
“This is a fantastic piece of engineering,” said Ted Norris, U-M professor of electrical engineering and computer science and director of the U-M Center for Photonic and Multiscale Nanomaterials. “It gets right to the central issue in photoconductive terahertz devices, which is collecting all the charge. Since every application benefits from increased sensitivity, for example, reduced data acquisition time or increased standoff distance, I expect this approach to be implemented widely.”
The research was funded by the Michigan Space Grant Consortium, Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency, National Science Foundation, Office of Naval Research and Army Research Office.