Do-it-yourself invisibility cloaking with 3D printing
May 15, 2013
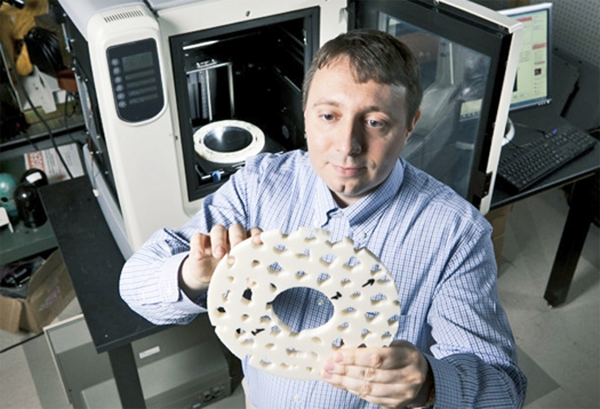
Yaroslav Urzhumov and the 3D-printed invisibility cloak (credit: Duke University)
Seven years ago, Duke University engineers demonstrated the first working invisibility cloak in complex laboratory experiments. Now it appears creating a simple cloak has become a lot simpler, by using a 3D printer..
Yaroslav Urzhumov, assistant research professor in electrical and computer engineering at Duke’s Pratt School of Engineering, said producing a cloak in this fashion is inexpensive and easy.
He and his team made a small one at Duke that looks like a Frisbee disc made out of Swiss cheese.
Algorithms determined the location, size and shape of the holes to deflect microwave beams. The fabrication process takes from three to seven hours.
Just like the 2006 cloak, the newer version deflects microwave beams, but researchers feel confident that in the not-so-distant future, the cloak can work for higher wavelengths, including visible light.
“We believe this approach is a way towards optical cloaking, including visible and infrared,” Urzhumov said. “And nanotechnology is available to make these cloaks from transparent polymers or glass. The properties of transparent polymers and glasses are not that different from what we have in our polymer at microwave frequencies.”
The disk-like cloak has an open area in its center where the researchers placed an opaque object. When microwave beams were aimed at the object through the side of the disk, the cloak made it appear that the object was not there.
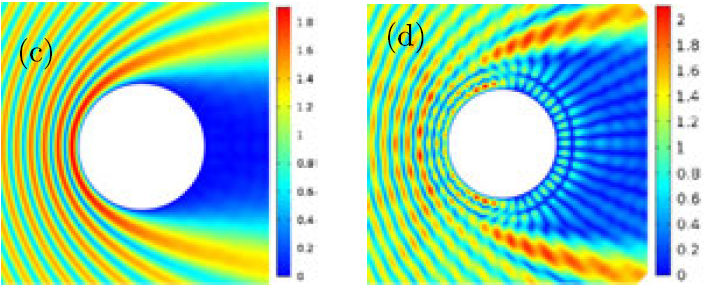
Field intensity for an uncloaked cylinder (c) compared to a cloaked cylinder (d) (simulations) (credit: Yaroslav Urzhumov et al./Optics Letters)
“The design of the cloak eliminates the ‘shadow’ that would be cast, and suppresses the scattering from the object that would be expected,” said Urzhumov. “In effect, the bright, highly reflective object, like a metal cylinder, is made invisible. The microwaves are carefully guided by a thin dielectric shell and then re-radiated back into free space on the shadow side of the cloak.”
Urzhumov said that theoretically, the technique can be used to create much larger devices.
“Computer simulations make me believe that it is possible to create a similar polymer-based cloaking layer as thin as one inch wrapped around a massive object several meters in diameter,” he said. “I have run some simulations that seem to confirm this point.”
The research was supported by the U.S. Army Research Office through a Multidisciplinary University Research Initiative grant.