How mass extinctions can accelerate robot evolution
August 31, 2015
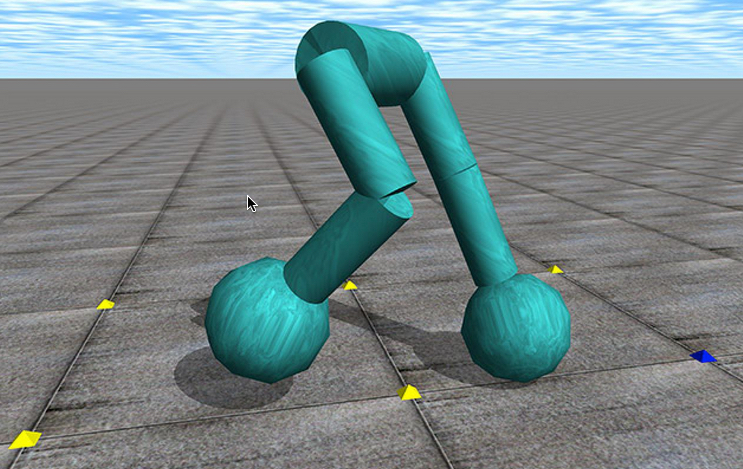
At the start of the simulation, a biped robot controlled by a computationally evolved brain stands upright on a 16 meter by 16 meter surface. The simulation proceeds until the robot falls or until 15 seconds have elapsed. (credit: Joel Lehman)
Robots evolve more quickly and efficiently after a virtual mass extinction modeled after real-life disasters, such as the one that killed off the dinosaurs, computer scientists at The University of Texas at Austin have found.
Mass extinctions speed up evolution by unleashing new creativity in adaptations.
Computer scientists Risto Miikkulainen and Joel Lehman co-authored the study published in an open-access paper in the journal PLOS One.
“Focused destruction can lead to surprising outcomes,” said Miikkulainen, a professor of computer science at UT Austin. “Sometimes you have to develop something that seems objectively worse in order to develop the tools you need to get better.”
Survival of the evolvable
In biology, mass extinctions are known for being highly destructive, erasing a lot of genetic material from the tree of life. But some evolutionary biologists hypothesize that extinction events actually accelerate evolution by promoting those lineages that are the most evolvable, meaning ones that can quickly create useful new features and abilities.
Miikkulainen and Lehman found that, at least with robots, this is the case.
For years, computer scientists have used computer algorithms inspired by evolution to train simulated robot brains, called neural networks, to improve at a task from one generation to the next. But could mass destruction speed things up?
To find out, they connected neural networks to simulated robotic legs with the goal of evolving a robot that could walk smoothly and stably. As with real evolution, random mutations were introduced through the computational evolution process. The scientists created many different niches so that a wide range of novel features and abilities would come about.
Pruning to achieve super-robots
After hundreds of generations, a wide range of robotic behaviors had evolved to fill these niches, many of which were not directly useful for walking. Then the researchers randomly killed off the robots in 90 percent of the niches, mimicking a mass extinction.
After several such cycles of evolution and extinction, they discovered that the lineages that survived were the most evolvable and, therefore, had the greatest potential to produce new behaviors. Not only that, but overall, better solutions to the task of walking were evolved in simulations with mass extinctions, compared with simulations without them.
Practical applications of the research could include the development of robots that can better overcome obstacles (such as robots searching for survivors in earthquake rubble, exploring Mars or navigating a minefield) and human-like game agents.
“This is a good example of how evolution produces great things in indirect, meandering ways,” explains Lehman, a former postdoctoral researcher in Miikkulainen’s lab, now at the IT University of Copenhagen. He and a former student of Miikkulainen’s at UT Austin, Kenneth Stanley, recently published a popular science book about evolutionary meandering, The Myth of the Objective: Why Greatness Cannot Be Planned. “Even destruction can be leveraged for evolutionary creativity,” Lehman says.
This research was funded by the National Science Foundation (NSF), National Institutes of Health and UT Austin’s Freshman Research Initiative. Funding from NSF was provided through grants to BEACON, a multi-university center established to study evolution in action in natural and virtual settings. The University of Texas at Austin is a member of BEACON. Evolutionary biologists in BEACON assisted Miikkulainen and Lehman in designing the research project and interpreting the results.
Abstract of Extinction Events Can Accelerate Evolution
Extinction events impact the trajectory of biological evolution significantly. They are often viewed as upheavals to the evolutionary process. In contrast, this paper supports the hypothesis that although they are unpredictably destructive, extinction events may in the long term accelerate evolution by increasing evolvability. In particular, if extinction events extinguish indiscriminately many ways of life, indirectly they may select for the ability to expand rapidly through vacated niches. Lineages with such an ability are more likely to persist through multiple extinctions. Lending computational support for this hypothesis, this paper shows how increased evolvability will result from simulated extinction events in two computational models of evolved behavior. The conclusion is that although they are destructive in the short term, extinction events may make evolution more prolific in the long term.