How the brain forms time-linked memories
January 28, 2014
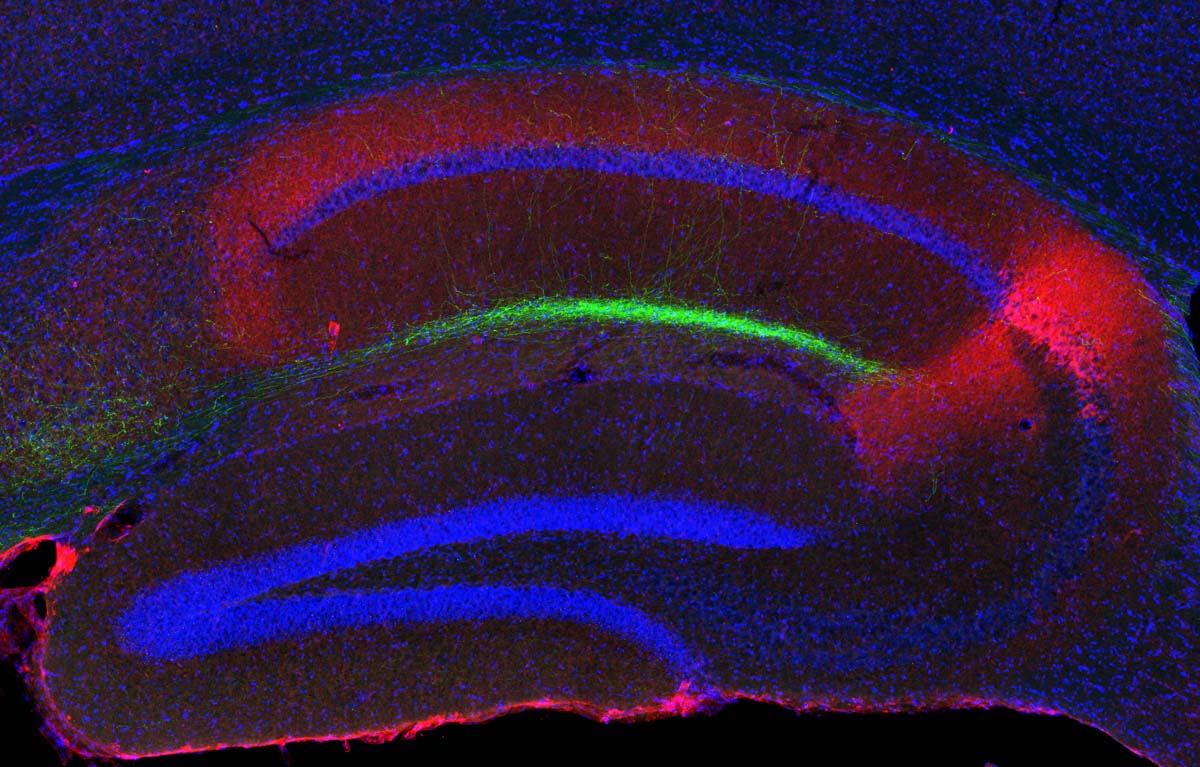
This cross-section of the hippocampus shows island cells (green) projecting to the CA1 region of the hippocampus (credit: Takashi Kitamura)
MIT neuroscientists have discovered how two neural circuits in the brain work together to control the formation of time-linked memories, such as the sound of skidding tires, followed by a car crash.*
This is a critical ability that helps the brain to determine when it needs to take action to defend against a potential threat, says Susumu Tonegawa, the Picower Professor of Biology and Neuroscience and senior author of a paper describing the findings in the Jan. 23 issue of Science.
“It’s important for us to be able to associate things that happen with some temporal gap,” says Tonegawa, who is a member of MIT’s Picower Institute for Learning and Memory. “For animals it is very useful to know what events they should associate, and what not to associate.”
The interaction of these two circuits allows the brain to maintain a balance between becoming too easily paralyzed with fear and being too careless, which could result in being caught off guard by a predator or other threat.
The paper’s lead authors are Picower Institute postdocs Takashi Kitamura and Michele Pignatelli.
Memories of events, known as episodic memories, always contain three elements — what, where, and when. Those memories are created in a brain structure called the hippocampus, which must coordinate each of these three elements.
To form episodic memories, the hippocampus also communicates with the region of the cerebral cortex just outside the hippocampus, known as the entorhinal cortex. The entorhinal cortex, which has several layers, receives sensory information, such as sights and sounds, from sensory processing areas of the brain and sends the information on to the hippocampus.
Previous research has revealed a great deal about how the brain links the place and object components of memory. Certain neurons in the hippocampus, known as place cells, are specialized to fire when an animal is in a specific location, and also when the animal is remembering that location. However, when it comes to associating objects and time, “our understanding has fallen behind,” Tonegawa says. “Something is known, but relatively little compared to the object-place mechanism.”
The new Science paper builds on a 2011 study from Tonegawa’s lab in which he identified a brain circuit necessary for mice to link memories of two events — a tone and a mild electric shock — that occur up to 20 seconds apart. This circuit connects layer 3 of the entorhinal cortex to the CA1 region of the hippocampus. When that circuit, known as the monosynaptic circuit, was disrupted, the animals did not learn to fear the tone.
In the new paper, the researchers report the discovery of a previously unknown circuit that suppresses the monosynaptic circuit. This signal originates in a type of excitatory neurons discovered in Tonegawa’s lab, dubbed “island cells” because they form circular clusters within layer 2. Those cells stimulate inhibitory neurons in CA1 that suppress the set of excitatory CA1 neurons that are activated by the monosynaptic circuit.
This circuit creates a counterbalance that limits the window of opportunity for two events to become linked. “This pathway might provide a mechanism for preventing constant learning of unimportant temporal associations,” says Michael Hasselmo, a professor of psychology at Boston University who was not part of the research team.
The findings are “an important demonstration of the functional role of different populations of neurons in entorhinal cortex that provide input to the hippocampus,” Hasselmo adds.
Deciphering circuits
The researchers used optogenetics, a technology that allows specific populations of neurons to be turned on or off with light, to demonstrate the interplay of these two circuits.
In normal mice, the maximum time gap between events that can be linked is about 20 seconds, but the researchers could lengthen that period by either boosting activity of layer 3 cells or suppressing layer 2 island cells. Conversely, they could shorten the window of opportunity by inhibiting layer 3 cells or stimulating input from layer 2 island cells, which both result in turning down CA1 activity.
The researchers hypothesize that prolonged CA1 activity keeps the memory of the tone alive long enough so that it is still present when the shock takes place, allowing the two memories to be linked. They are now investigating whether CA1 neurons remain active throughout the entire gap between events.
The research was funded by the RIKEN Brain Science Institute, the Howard Hughes Medical Institute, and the JPB Foundation.
* In related research reported today, other MIT researchers scanned individuals’ brains as they looked at different images and were able to pinpoint, to the millisecond, when the brain recognizes and categorizes an object, and where these processes occur.
Abstract of Science paper
Episodic memory requires associations of temporally discontiguous events. In the entorhinal-hippocampal network, temporal associations are driven by a direct pathway from layer III of the medial entorhinal cortex (MECIII) to the hippocampal CA1 region. However, the identification of neural circuits that regulate this association has remained unknown. In layer II of entorhinal cortex (ECII), we report clusters of excitatory neurons called island cells, which appear in a curvilinear matrix of bulb-like structures, directly project to CA1 and activate interneurons that target the distal dendrites of CA1 pyramidal neurons. Island cells suppress the excitatory MECIII input through the feedforward inhibition to control the strength and duration of temporal association in trace fear memory. Together, the two EC inputs comprise a control circuit for temporal association memory.