Implanted Sensor Could Provide Clues to Brain Chemistry
February 17, 2010 | Source: Technology Review
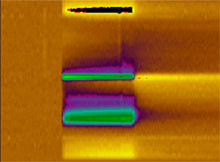
Release of dopamine (lower green and purple band) and adenosine (upper green and purple band) chemical messengers (Kendall H. Lee, MD, PhD, director of Mayo Neural Engineering Laboratories, and Kevin Bennet, Chair of Mayo Division of Engineering)
The device consists of a custom-designed sensor electrode that is implanted along with the stimulating electrode, a microprocessor, a Bluetooth module to send data to a computer, and a battery.