Magnetic fields provide a lower-power, more secure wireless body network
September 1, 2015
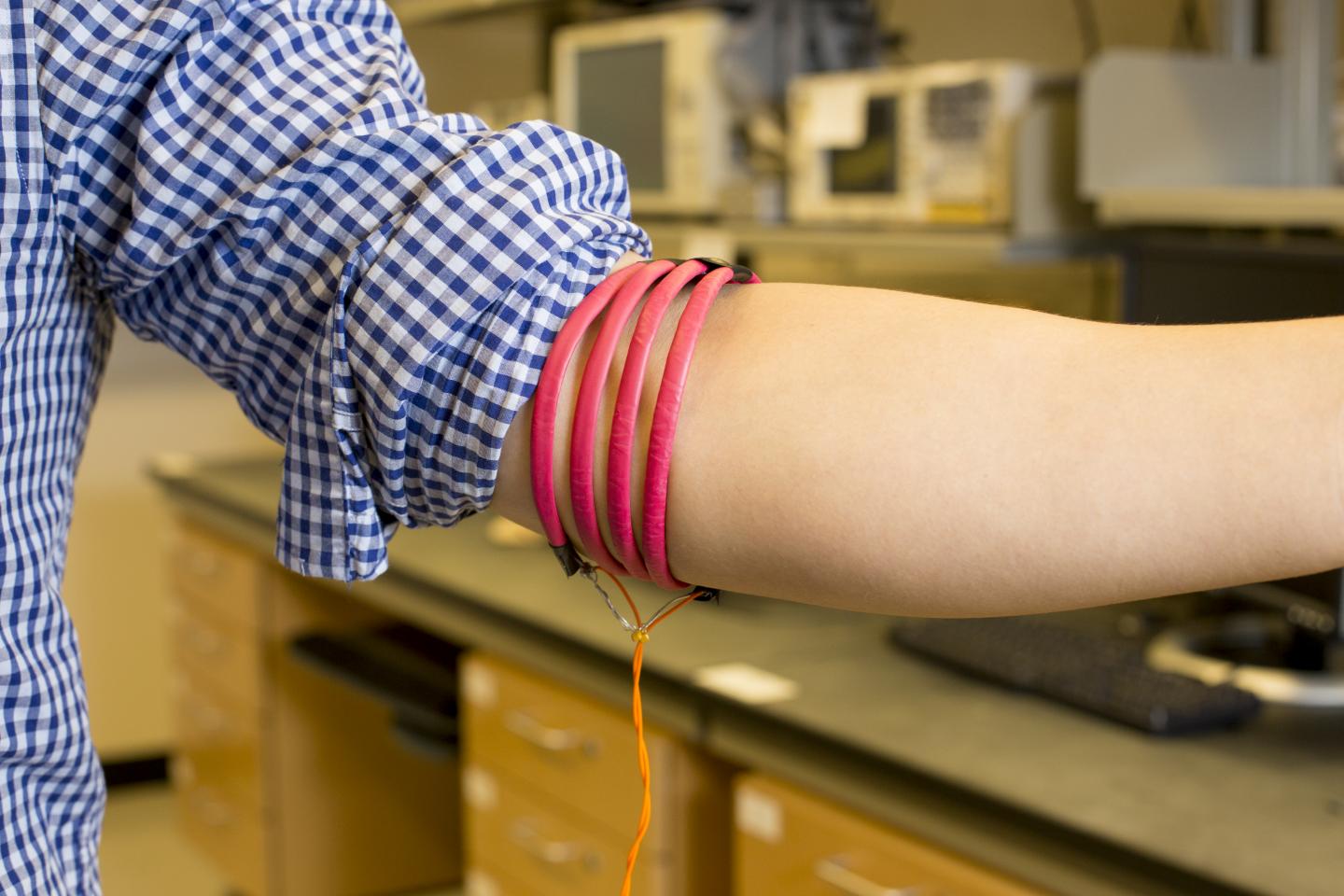

This is a prototype of the magnetic field human body communication, developed at UC San Diego, consists of magnetic-field-generating coils wrapped around three parts of the body, including the head, arm and leg (credit: Jacobs School of Engineering, UC San Diego)
A new wireless communication technique that works by sending magnetic signals through the human body could offer a lower power and more secure way to communicate information between wearable electronic devices than Bluetooth, according to electrical engineers at the University of California, San Diego.
While this work is still a proof-of-concept demonstration, researchers envision developing it into an ultra-low-power wireless system that can easily transmit information around the human body. One use would be a wireless sensor network for full-body health monitoring.
“In the future, people are going to be wearing more electronics, such as smart watches, fitness trackers and health monitors. All of these devices will need to communicate information with each other. Currently, these devices transmit information using Bluetooth radios, which use a lot of power to communicate. We’re trying to find new ways to communicate information around the human body that use much less power,” said Patrick Mercier, a professor in the Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering at UC San Diego who led the study. Mercier also serves as the co-director of the UC San Diego Center for Wearable Sensors.
Bluetooth technology uses high-frequency electromagnetic radiation to transmit data; at those frequencies, radio signals do not easily pass through the human body, so they require a power boost to help overcome this signal obstruction, or “path loss.”
Lower power consumption
In this study, electrical engineers demonstrated a technique called “magnetic field human body communication” (mHBC), which uses the body as a vehicle to deliver magnetic energy between electronic devices. An advantage of this system is that magnetic fields are able to pass freely through biological tissues, so signals are communicated with much lower path losses and potentially, much lower power consumption.
In their experiments, researchers demonstrated that the magnetic communication link works well on the body, but they did not test the technique’s power consumption. However, the showed that the path losses associated with magnetic field human body communication are upwards of 10 million times lower than those associated with Bluetooth radios.
“This technique, to our knowledge, achieves the lowest path losses out of any wireless human body communication system that’s been demonstrated so far. This technique will allow us to build much lower power wearable devices,” said Mercier.
Lower power consumption also leads to longer battery life. “A problem with wearable devices like smart watches is that they have short operating times because they are limited to using small batteries. With this magnetic field human body communication system, we hope to significantly reduce power consumption as well as how frequently users need to recharge their devices,” said Jiwoong Park, a Ph.D student in Mercier’s Energy-Efficient Microsystems Lab at the UC San Diego Jacobs School of Engineering and first author of the study.
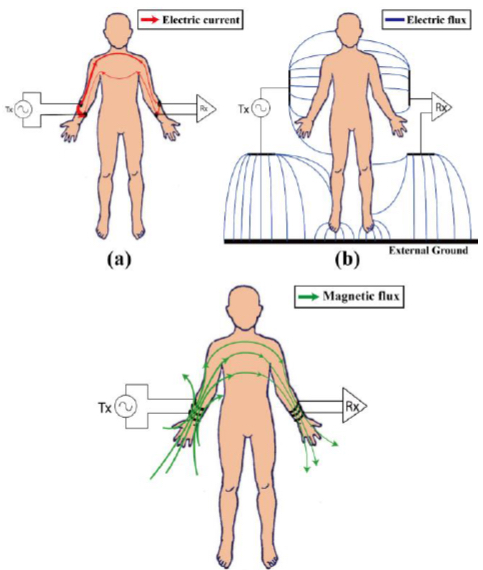
Human body communication schemes: (a) galvanic coupling using electric fields, (b) capacitive coupling using electric fields, and (c) the proposed magnetic resonant coupling scheme (credit: Jiwoong Park and Patrick P. Mercier)
The engineers presented their findings Aug. 26 at the 37th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society in Milan, Italy. In a forthcoming paper, they also compare their mHBC scheme to two earlier electric field human body communication (eHBC) schemes: galvanic coupling (using electric currents) and capacitive eHBC, also known as a wireless Body Area Network (using near-field radio frequencies); both have high path loss and other problems, they note.
Better security
The researchers also pointed out that this technique does not pose any serious health risks. Since this technique is intended for applications in ultra low power communication systems, the transmitting power of the magnetic signals sent through the body is expected to be many times lower than that of MRI scanners and wireless implant devices.
Another potential advantage of magnetic field human body communication is that it could offer more security than Bluetooth networks. Because Bluetooth radio communicates data over the air, anyone standing within 30 feet can potentially eavesdrop on that communication link. On the other hand, magnetic field human body communication employs the human body as a communication medium, making the communication link less vulnerable to eavesdropping. With this technique, researchers demonstrated that magnetic communication is strong on the body but dramatically decreases off the body. To put this in the context of a personal full-body wireless communication network, information would neither be radiated off the body nor be transmitted from one person to another.
“Increased privacy is desirable when you’re using your wearable devices to transmit information about your health,” said Park.
A proof-of-concept prototype
The researchers built a prototype to demonstrate the magnetic field human body communication technique. The prototype consists of copper wires insulated with PVC tubes. On one end, the copper wires are hooked up to an external analyzer and on the other end, the wires are wrapped in coils around three areas of the body: the head, arms and legs. These coils serve as sources for magnetic fields and are able to send magnetic signals from one part of the body to another using the body as a guide. With this prototype, researchers were able to demonstrate and measure low path loss communication from arm to arm, from arm to head, and from arm to leg.
Researchers noted that a limitation of this technique is that magnetic fields require circular geometries in order to propagate through the human body. Devices like smart watches, headbands and belts will all work well using magnetic field human body communication, but not a small patch that is stuck on the chest and used to measure heart rate, for example. As long as the wearable application can wrap around a part of the body, it should work just fine with this technique, researchers explained.
UPDATE Sept. 5, 2015 — ADDED (with illustration): In a forthcoming paper, they also compare their mHBC scheme to two earlier electric field human body communication (eHBC) schemes: galvanic coupling (using electric currents) and capacitive eHBC, also known as a wireless Body Area Network (using near-field radio frequencies); both have high path loss and other problems, they note.