New e-reader paper discovered that’s fast enough for video yet cheap enough to be disposable
November 23, 2010
A discovery by University of Cincinnati engineering researcher Andrew Steckl could revolutionize display technology with e-paper that’s fast enough for video yet cheap enough to be disposable.
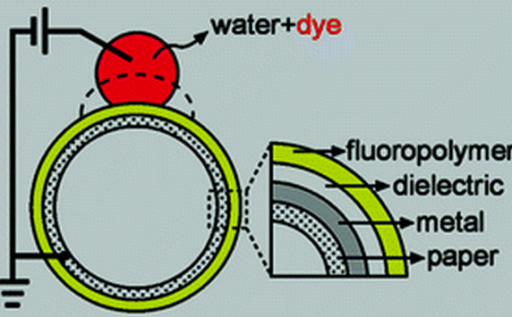
He and his team have demonstrated that paper could be used as a flexible host material for an electrowetting device. Electrowetting (EW) involves applying an electric field to colored droplets within a display in order to reveal content such as type, photographs and video.
The discovery has far-reaching implications, considering that other popular e-readers on the market such as the Kindle and iPad rely on complex circuitry printed over a rigid glass substrate.
“One of the main goals of e-paper is to replicate the look and feel of actual ink on paper,” the researchers stated in a cover story in ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. Importantly, they found that the performance of the electrowetting device on paper is equivalent to that of glass, which is the gold standard in the field.
“It is pretty exciting,” said Steckl. “With the right paper, the right process and the right device fabrication technique, you can get results that are as good as you would get on glass, and our results are good enough for a video-style e-reader.”
Steckl imagines a future device that is rollable, feels like paper yet delivers books, news and even high-resolution color video in bright-light conditions.
“Nothing looks better than paper for reading,” said Steckl, an Ohio Eminent Scholar. “We hope to have something that would actually look like paper but behave like a computer monitor in terms of its ability to store information. We would have something that is very cheap, very fast, full-color and at the end of the day or the end of the week, you could pitch it into the trash.”
Disposing of a paper-based e-reader, Steckl points out, is also far simpler in terms of the environmental impact.
“In general, this is an elegant method for reducing device complexity and cost, resulting in one-time-use devices that can be totally disposed after use,” the researchers pointed out.
Steckl’s goal is attract commercial interest in the technology for next-stage development, which he expects will take three to five years to get to market.
Ref.: Electrowetting on Paper for Electronic Paper Display, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces
The work was supported, in part, by a grant from the National Science Foundation and was conducted at the Nanoelectronics Laboratory at the University of Cincinnati College of Engineering and Applied Science.
Adapted from materials provided by the University of Cincinnati