Tiny wireless LED activates neurons to release dopamine
April 15, 2013

This implantable LED light can activate brain cells to release dopamine and is smaller than the eye of a needle (credit: John A Rogers and Michael R. Bruchas/Washington University)
Researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis and the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign have developed tiny devices containing light-emitting diodes (LEDs) the size of individual neurons that activate brain cells with light.
“This strategy should allow us to identify and map brain circuits involved in complex behaviors related to sleep, depression, addiction, and anxiety,” says co-principal investigator Michael R. Bruchas, PhD, assistant professor of anesthesiology at Washington University.
“Understanding which populations of neurons are involved in these complex behaviors may allow us to target specific brain cells that malfunction in depression, pain, addiction and other disorders.”
For the study, Washington University neuroscientists teamed with engineers at the University of Illinois to design multicolored microscale, inorganic light-emitting diodes (µILEDs) that are just 6.45 microns (micrometers, or millionths of a meter) thick (thinner than a human hair) and and 50 × 50 µm square. The µILEDs are less than one-thousandth the size of conventional LEDs (typically 100 mm thick with lateral dimensions of 1 mm square).
The small sizes of µILEDs allow for spatially precise cellular-scale delivery of photons, highly effective
thermal management, reduced tissue damage, and minimized inflammation for prolonged use
in vivo.
This was the first application of the devices in optogenetics, which uses light to stimulate targeted pathways in the brain. The scientists implanted them into the brains of mice that had been genetically engineered so that some of their brain cells could be activated and controlled with light.
Although a number of important pathways in the brain can be studied with optogenetics, many neuroscientists have struggled with the engineering challenge of delivering light to precise locations deep in the brain. Most methods have tethered animals to lasers with fiber optic cables, limiting their movement and altering natural behaviors.
But with the new devices, the mice freely moved about and were able to explore a maze or scamper on a wheel. The electronic µLEDs are housed in a tiny fiber implanted deep in the brain. Moving freely is important to the device’s ability to activate the proper neurons, according to John A. Rogers, PhD, professor of materials science and engineering at the University of Illinois.
“You want to be able to deliver the light down into the depth of the brain,” Rogers says. “We think we’ve come up with some powerful strategies that involve ultra-miniaturized devices that can deliver light signals deep into the brain and into other organs in the future.”
Stimulating neurons in the brain wirelessly
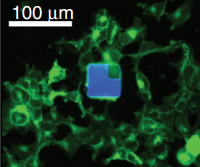
An epifluorescent image of a µLED device among cultured human embryonic kidney cells, to illustrate the similar sizes (credit: John A Rogers and Michael R. Bruchas/Washington University/Science)
Using light from the cellular-sized µLEDs to stimulate dopamine-producing cells in the brain, the investigators taught the mice to poke their noses through a specific hole in a maze.
Each time a mouse would poke its nose through the hole, that would trigger the system to wirelessly activate the µLEDs in the implanted device, which then would emit light, causing neurons to release dopamine, a chemical related to the brain’s natural reward system.
“We used the LED devices to activate networks of brain cells that are influenced by the things you would find rewarding in life, like sex or chocolate,” says co-first author Jordan G. McCall, a neuroscience graduate student in Washington University’s Division of Biology and Biomedical Sciences.
“When the brain cells were activated to release dopamine, the mice quickly learned to poke their noses through the hole even though they didn’t receive any food as a reward. They also developed an associated preference for the area near the hole, and they tended to hang around that part of the maze.”
The researchers believe the LED implants may be useful in other types of neuroscience studies or may even be applied to different organs. Related devices already are being used to stimulate peripheral nerves for pain management.
Other devices with LEDs of multiple colors may be able to activate and control several neural circuits at once. In addition to the tiny µLEDs, the devices also carry miniaturized precision optical, thermal, and electrophysiological sensors for detecting temperature and electrical activity within the brain, along with actuators.
Treating brain disorders
Bruchas and his colleagues already have begun other studies of mice, using the LED devices to manipulate neural circuits that are involved in social behaviors. This could help scientists better understand what goes on in the brain in disorders such as depression and anxiety.
“We believe these devices will allow us to study complex stress and social interaction behaviors,” Bruchas explains. “This technology enables us to map neural circuits with respect to things like stress and pain much more effectively.”
The wireless, microLED implant devices represent the combined efforts of Bruchas and Rogers. Last year, along with Robert W. Gereau IV, PhD, professor of anesthesiology, they were awarded an NIH Director’s Transformative Research Project award to develop and conduct studies using novel device development and optogenetics.
Funding for this research comes from the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS), the National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA) and the NIH Common Fund of the National Institutes of Health (NIH). Other funding comes from the McDonnell Center for Systems Neuroscience, a National Security Science and Engineering Faculty Fellowship of Energy, a US Department of Energy Division of Material Sciences Award, and the Materials Research Laboratory and Center for Microanalysis of Materials.