Growing number of chemicals linked with brain disorders in children
February 18, 2014
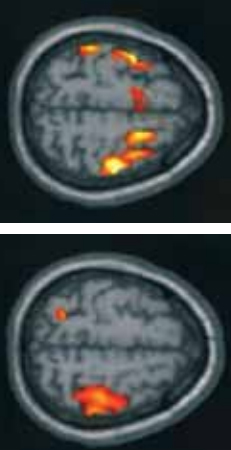
Functional MRI scans of people exposed prenatally to excess amounts of methylmercury showed abnormally expanded activation of brain regions in response to sensory stimulation and motor tasks. Average activation during finger tapping with the left hand in three adolescents with increased prenatal methylmercury exposure (top) was bilateral. For the three control adolescents (bottom) participants activate the premotor and motor cortices on the right. (Credit: Philippe Grandjean, Philip Landrigan, Lancet Neurology
Toxic chemicals may be triggering the recent increases in neurodevelopmental disabilities among children — such as autism, attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder, and dyslexia — according to a new study from Harvard School of Public Health (HSPH) and Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai. The researchers say a new global prevention strategy to control the use of these substances is urgently needed.
The report was published online February 15, 2014 in Lancet Neurology.
“The greatest concern is the large numbers of children who are affected by toxic damage to brain development in the absence of a formal diagnosis. They suffer reduced attention span, delayed development, and poor school performance. Industrial chemicals are now emerging as likely causes,” said Philippe Grandjean, adjunct professor of environmental health at HSPH.
The report follows up on a similar review conducted by the authors in 2006 that identified five industrial chemicals as “developmental neurotoxicants,” or chemicals that can cause brain deficits.
The new study offers updated findings about those chemicals and adds information on six newly recognized ones, including manganese, fluoride, chlorpyrifos and DDT (pesticides), tetrachloroethylene (a solvent), and the polybrominated diphenyl ethers (flame retardants).
The study outlines possible links between these newly recognized neurotoxicants and negative health effects on children, including:
- Manganese is associated with diminished intellectual function and impaired motor skills
- Solvents are linked to hyperactivity and aggressive behavior
- Certain types of pesticides may cause cognitive delays
Grandjean and co-author Philip Landrigan, Dean for Global Health at Mount Sinai, also forecast that many more chemicals than the known dozen or so identified as neurotoxicants contribute to a “silent pandemic” of neurobehavioral deficits that is eroding intelligence, disrupting behaviors, and damaging societies.
But controlling this pandemic is difficult because of a scarcity of data to guide prevention and the huge amount of proof needed for government regulation. “Very few chemicals have been regulated as a result of developmental neurotoxicity,” they write.
The authors say it’s crucial to control the use of these chemicals to protect children’s brain development worldwide. They propose mandatory testing of industrial chemicals and the formation of a new international clearinghouse to evaluate industrial chemicals for potential developmental neurotoxicity.
“The problem is international in scope, and the solution must therefore also be international,” said Grandjean.
“We have the methods in place to test industrial chemicals for harmful effects on children’s brain development — now is the time to make that testing mandatory.”
Funding for the study came from the National Institute for Environmental Health Sciences of the National Institutes of Health.
Abstract of Lancet Neurology paper
Neurodevelopmental disabilities, including autism, attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder, dyslexia, and other cognitive impairments, affect millions of children worldwide, and some diagnoses seem to be increasing in frequency. Industrial chemicals that injure the developing brain are among the known causes for this rise in prevalence. In 2006, we did a systematic review and identified five industrial chemicals as developmental neurotoxicants: lead, methylmercury, polychlorinated biphenyls, arsenic, and toluene. Since 2006, epidemiological studies have documented six additional developmental neurotoxicants—manganese, fluoride, chlorpyrifos, dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane, tetrachloroethylene, and the polybrominated diphenyl ethers. We postulate that even more neurotoxicants remain undiscovered. To control the pandemic of developmental neurotoxicity, we propose a global prevention strategy. Untested chemicals should not be presumed to be safe to brain development, and chemicals in existing use and all new chemicals must therefore be tested for developmental neurotoxicity. To coordinate these efforts and to accelerate translation of science into prevention, we propose the urgent formation of a new international clearinghouse.