How to identify which cancer drugs work best for each patient
April 22, 2015
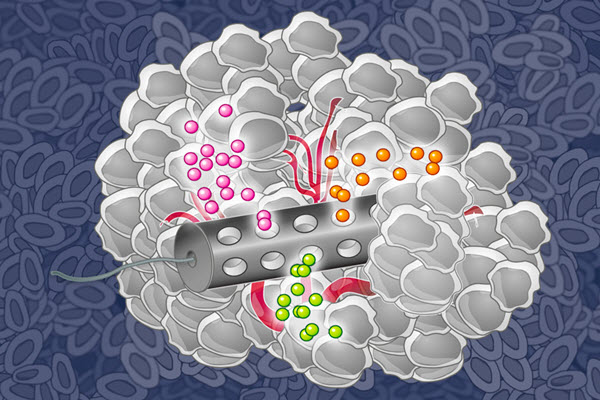
MIT chemical engineers have designed an implantable device that can deliver many drugs at once, allowing researchers to determine which drugs are the most effective against a patient’s tumor (credit: Eric Smith, edited by Jose-Luis Olivares/MIT))
More than 100 drugs have been approved to treat cancer, but predicting which ones will help a particular patient is an inexact science at best. Now a new implantable device developed at MIT can carry small doses of up to 30 different drugs promises to allow researchers to measure how effectively each one kills the patient’s cancer cells.
Such a device could eliminate much of the guesswork now involved in choosing cancer treatments, says Oliver Jonas, a postdoc at MIT’s Koch Institute for Integrative Cancer Research and lead author of a paper describing the device in the April 22 issue of Science Translational Medicine.
“You can use it to test a patient for a range of available drugs, and pick the one that works best,” Jonas says.
The paper’s senior authors are Robert Langer, the David H. Koch Professor at MIT and a member of the Koch Institute, the Institute for Medical Engineering and Science, and the Department of Chemical Engineering; and Michael Cima, the David H. Koch Professor of Engineering at MIT and a member of the Koch Institute and the Department of Materials Science and Engineering.
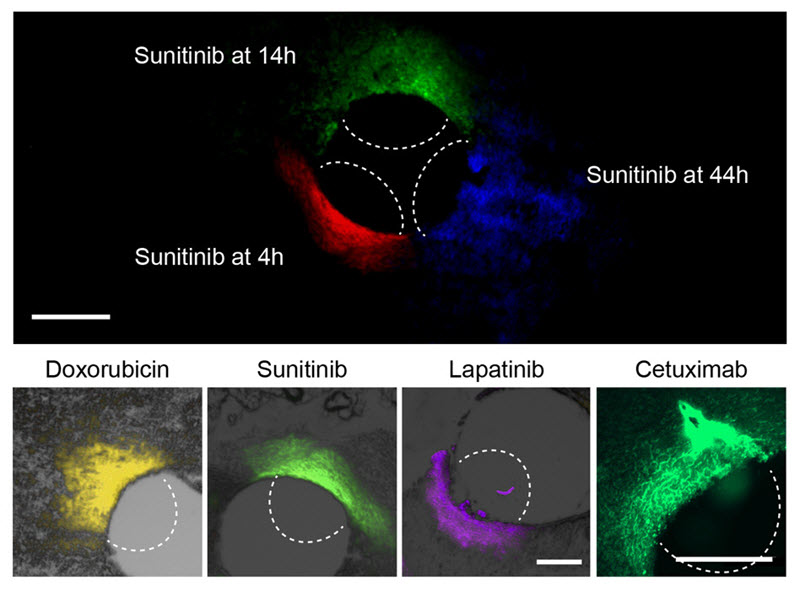
At top, the researchers can use this device to measure how far a given drug spreads over time. At bottom, they used the device to measure the spread of four different cancer drugs. (credit: Oliver Jonas et al/Science)
Putting the lab in the patient
Most of the commonly used cancer drugs work by damaging DNA or otherwise interfering with cell function. Recently, scientists have also developed more targeted drugs designed instead to only kill tumor cells that carry a specific genetic mutation. However, it is usually difficult to predict whether a particular drug will be effective in an individual patient.
In some cases, doctors extract tumor cells, grow them in a lab dish, and treat them with different drugs to see which ones are most effective. However, this process removes the cells from their natural environment, which can play an important role in how a tumor responds to drug treatment, Jonas says.
“The approach that we thought would be good to try is to essentially put the lab into the patient,” he says. “It’s safe and you can do all of your sensitivity testing in the native microenvironment.”
The device, made from a stiff, crystalline polymer, can be implanted in a patient’s tumor using a biopsy needle. After implantation, drugs seep 200 to 300 micrometers into the tumor, but do not overlap with each other. Any type of drug can go into the reservoir, and the researchers can formulate the drugs so that the doses that reach the cancer cells are similar to what they would receive if the drug were given by typical delivery methods such as intravenous injection.
After one day of drug exposure, the implant is removed, along with a small sample of the tumor tissue surrounding it, and the researchers analyze the drug effects by slicing up the tissue sample and staining it with antibodies that can detect markers of cell death or proliferation.
Ranking cancer drugs
To test the device, the researchers implanted it in mice that had been grafted with human prostate, breast, and melanoma tumors. These tumors are known to have varying sensitivity to different cancer drugs, and the MIT team’s results corresponded to those previously seen differences.
The researchers then tested the device with a type of breast cancer known as triple negative, which lacks the three most common breast cancer markers: estrogen receptor, progesterone receptor, and Her2. This form of cancer is particularly aggressive, and none of the drugs used against it are targeted to a specific genetic marker.
Using the device, the researchers found that triple negative tumors responded differently to five of the drugs commonly used to treat them. The most effective was paclitaxel, followed by doxorubicin, cisplatin, gemcitabine, and lapatinib. They found the same results when delivering these drugs by intravenous injection, suggesting that the device is an accurate predictor of drug sensitivity.
In this study, the researchers compared single drugs to each other, but the device could also be used to test different drug combinations by putting two or three drugs into the same reservoir, Jonas says.
“This device could help us identify the best chemotherapy agents and combinations for every tumor prior to starting systemic administration of chemotherapy, as opposed to making choices based on population-based statistics. This has been a longstanding pursuit of the oncology community and an important step toward our goal of developing precision-based cancer therapy,” says Jose Baselga, chief medical officer at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center and an author of the paper.
The researchers are now working on ways to make the device easier to read while it is still inside the patient, allowing them to get results faster. They are also planning to launch a clinical trial in breast cancer patients next year.
Another possible application for this device is to guide the development and testing of new cancer drugs. Researchers could create several different variants of a promising compound and test them all at once in a small trial of human patients, allowing them to choose the best one to carry on to a larger clinical trial.
The research was funded by Kibur Medical and the National Cancer Institute. Other authors of the paper are Heather Landry, a graduate student at Harvard University; Jason Fuller, a former MIT graduate student; John Santini, president and CEO of ApoGen Biotechnologies; and Robert Tepper, a partner in Third Rock Ventures.
Abstract of An implantable microdevice to perform high-throughput in vivo drug sensitivity testing in tumors
Current anticancer chemotherapy relies on a limited set of in vitro or indirect prognostic markers of tumor response to available drugs. A more accurate analysis of drug sensitivity would involve studying tumor response in vivo. To this end, we have developed an implantable device that can perform drug sensitivity testing of several anticancer agents simultaneously inside the living tumor. The device contained reservoirs that released microdoses of single agents or drug combinations into spatially distinct regions of the tumor. The local drug concentrations were chosen to be representative of concentrations achieved during systemic treatment. Local efficacy and drug concentration profiles were evaluated for each drug or drug combination on the device, and the local efficacy was confirmed to be a predictor of systemic efficacy in vivo for multiple drugs and tumor models. Currently, up to 16 individual drugs or combinations can be assessed independently, without systemic drug exposure, through minimally invasive biopsy of a small region of a single tumor. This assay takes into consideration physiologic effects that contribute to drug response by allowing drugs to interact with the living tumor in its native microenvironment. Because these effects are crucial to predicting drug response, we envision that these devices will help identify optimal drug therapy before systemic treatment is initiated and could improve drug response prediction beyond the biomarkers and in vitro and ex vivo studies used today. These devices may also be used in clinical drug development to safely gather efficacy data on new compounds before pharmacological optimization.