Is this the first map of dark matter?
April 9, 2014
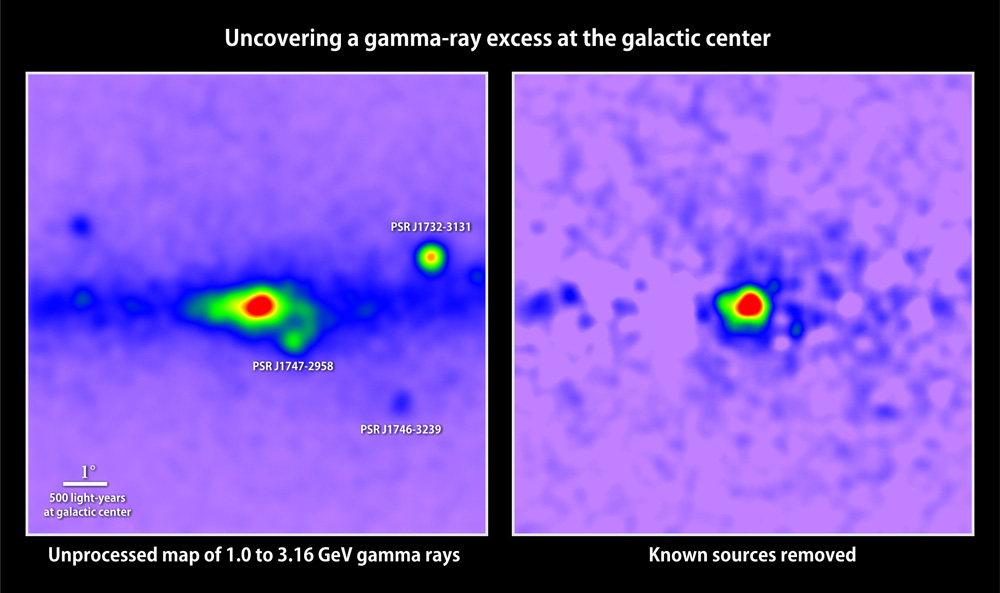
At left is a map of gamma rays with energies between 1 and 3.16 GeV detected in the galactic center by Fermi’s Large Area Telescope; red indicates the greatest number. Prominent pulsars are labeled. Removing all known gamma-ray sources (right) reveals excess emission that may arise from dark matter annihilations. (Credit: T. Linden, Univ. of Chicago)
A new study of gamma-ray light from the center of our galaxy makes the strongest case to date that some of this emission may arise from dark matter, an unknown substance making up most of the material universe. Using publicly available data from NASA‘s Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope, independent scientists at the Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory (Fermilab), the Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics (CfA), the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) and the University of Chicago have developed new maps showing that the galactic center produces more high-energy gamma rays than can be explained by known sources and that this excess emission is consistent with some forms of dark matter.
“The new maps allow us to analyze the excess and test whether more conventional explanations, such as the presence of undiscovered pulsars or cosmic-ray collisions on gas clouds, can account for it,” said Dan Hooper, an astrophysicist at Fermilab in Batavia, Ill., and a lead author of the study. “The signal we find cannot be explained by currently proposed alternatives and is in close agreement with the predictions of very simple dark matter models.”
Published on Apr 3, 2014 — This animation zooms into an image of the Milky Way, shown in visible light, and superimposes a gamma-ray map of the galactic center from NASA’s Fermi. Raw data transitions to a view with all known sources removed, revealing a gamma-ray excess hinting at the presence of dark matter. (Credit: NASA Goddard/A. Mellinger (Central Michigan Univ.) and T. Linden (Univ. of Chicago))
Removing the gamma-ray noise
The galactic center teems with gamma-ray sources, from interacting binary systems and isolated pulsars to supernova remnants and particles colliding with interstellar gas. It’s also where astronomers expect to find the galaxy’s highest density of dark matter, which only affects normal matter and radiation through its gravity. Large amounts of dark matter attract normal matter, forming a foundation upon which visible structures, like galaxies, are built.
No one knows the true nature of dark matter, but WIMPs, or Weakly Interacting Massive Particles, represent a leading class of candidates. Theorists have envisioned a wide range of WIMP types, some of which may either mutually annihilate or produce an intermediate, quickly decaying particle when they collide. Both of these pathways end with the production of gamma rays — the most energetic form of light — at energies within the detection range of Fermi’s Large Area Telescope (LAT).
When astronomers carefully subtract all known gamma-ray sources from the telescope observations of the galactic center, a patch of leftover emission remains. This excess appears most prominent at energies between 1 and 3 billion electron volts (GeV) — roughly a billion times greater than that of visible light — and extends outward at least 5,000 light-years from the galactic center.
Hooper and his colleagues conclude that annihilations of dark matter particles with a mass between 31 and 40 GeV provide a remarkable fit for the excess based on its gamma-ray spectrum, its symmetry around the galactic center, and its overall brightness. Writing in a paper submitted to the journal Physical Review D, the researchers say that these features are difficult to reconcile with other explanations proposed so far, although they note that plausible alternatives not requiring dark matter may yet materialize.
“Dark matter in this mass range can be probed by direct detection and by the Large Hadron Collider (LHC), so if this is dark matter, we’re already learning about its interactions from the lack of detection so far,” said co-author Tracy Slatyer, a theoretical physicist at MIT in Cambridge, Mass. “This is a very exciting signal, and while the case is not yet closed, in the future we might well look back and say this was where we saw dark matter annihilation for the first time.”
The researchers caution that it will take multiple sightings — in other astronomical objects, the LHC or in some of the direct-detection experiments now being conducted around the world — to validate their dark matter interpretation.
A small clue from dwarf galaxies
While the great amount of dark matter expected at the galactic center should produce a strong signal, competition from many other gamma-ray sources complicates any case for a detection. But turning the problem on its head provides another way to attack it. Instead of looking at the largest nearby collection of dark matter, look where the signal has fewer challenges.
Dwarf galaxies orbiting the Milky Way lack other types of gamma-ray emitters and contain large amounts of dark matter for their size – in fact, they’re the most dark-matter-dominated sources known. But there’s a tradeoff. Because they lie much farther away and contain much less total dark matter than the center of the Milky Way, dwarf galaxies produce a much weaker signal and require many years of observations to establish a secure detection.
For the past four years, the LAT team has been searching dwarf galaxies for hints of dark matter. The published results of these studies have set stringent limits on the mass ranges and interaction rates for many proposed WIMPs, even eliminating some models. In the study’s most recent results, published in Physical Review D on Feb. 11, the Fermi team took note of a small but provocative gamma-ray excess.
“There’s about a one-in-12 chance that what we’re seeing in the dwarf galaxies is not even a signal at all, just a fluctuation in the gamma-ray background,” explained Elliott Bloom, a member of the LAT Collaboration at the Kavli Institute for Particle Astrophysics and Cosmology, jointly located at the SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory and Stanford University.
If it’s real, the signal should grow stronger as Fermi acquires additional years of observations and as wide-field astronomical surveys discover new dwarfs. “If we ultimately see a significant signal,” he added, “it could be a very strong confirmation of the dark matter signal claimed in the galactic center.”
Abstract of arXiv paper
Past studies have identified a spatially extended excess of ~1-3 GeV gamma rays from the region surrounding the Galactic Center, consistent with the emission expected from annihilating dark matter. We revisit and scrutinize this signal with the intention of further constraining its characteristics and origin. By applying cuts to the Fermi event parameter CTBCORE, we suppress the tails of the point spread function and generate high resolution gamma-ray maps, enabling us to more easily separate the various gamma-ray components. Within these maps, we find the GeV excess to be robust and highly statistically significant, with a spectrum, angular distribution, and overall normalization that is in good agreement with that predicted by simple annihilating dark matter models. For example, the signal is very well fit by a 31-40 GeV dark matter particle annihilating to b quarks with an annihilation cross section of sigma v = (1.4-2.0) x 10^-26 cm^3/s (normalized to a local dark matter density of 0.3 GeV/cm^3). Furthermore, we confirm that the angular distribution of the excess is approximately spherically symmetric and centered around the dynamical center of the Milky Way (within ~0.05 degrees of Sgr A*), showing no sign of elongation along or perpendicular to the Galactic Plane. The signal is observed to extend to at least 10 degrees from the Galactic Center, disfavoring the possibility that this emission originates from millisecond pulsars.
Abstract of Physical Review D paper
The dwarf spheroidal satellite galaxies of the Milky Way are some of the most dark-matter-dominated objects known. Due to their proximity, high dark matter content, and lack of astrophysical backgrounds, dwarf spheroidal galaxies are widely considered to be among the most promising targets for the indirect detection of dark matter via γ rays. Here we report on γ-ray observations of 25 Milky Way dwarf spheroidal satellite galaxies based on 4 years of Fermi Large Area Telescope (LAT) data. None of the dwarf galaxies are significantly detected in γ rays, and we present γ-ray flux upper limits between 500 MeV and 500 GeV. We determine the dark matter content of 18 dwarf spheroidal galaxies from stellar kinematic data and combine LAT observations of 15 dwarf galaxies to constrain the dark matter annihilation cross section. We set some of the tightest constraints to date on the annihilation of dark matter particles with masses between 2 GeV and 10 TeV into prototypical standard model channels. We find these results to be robust against systematic uncertainties in the LAT instrument performance, diffuse γ-ray background modeling, and assumed dark matter density profile.