NASA discovers first near-Earth-size planet in the habitable zone around a Sun-like star
July 23, 2015
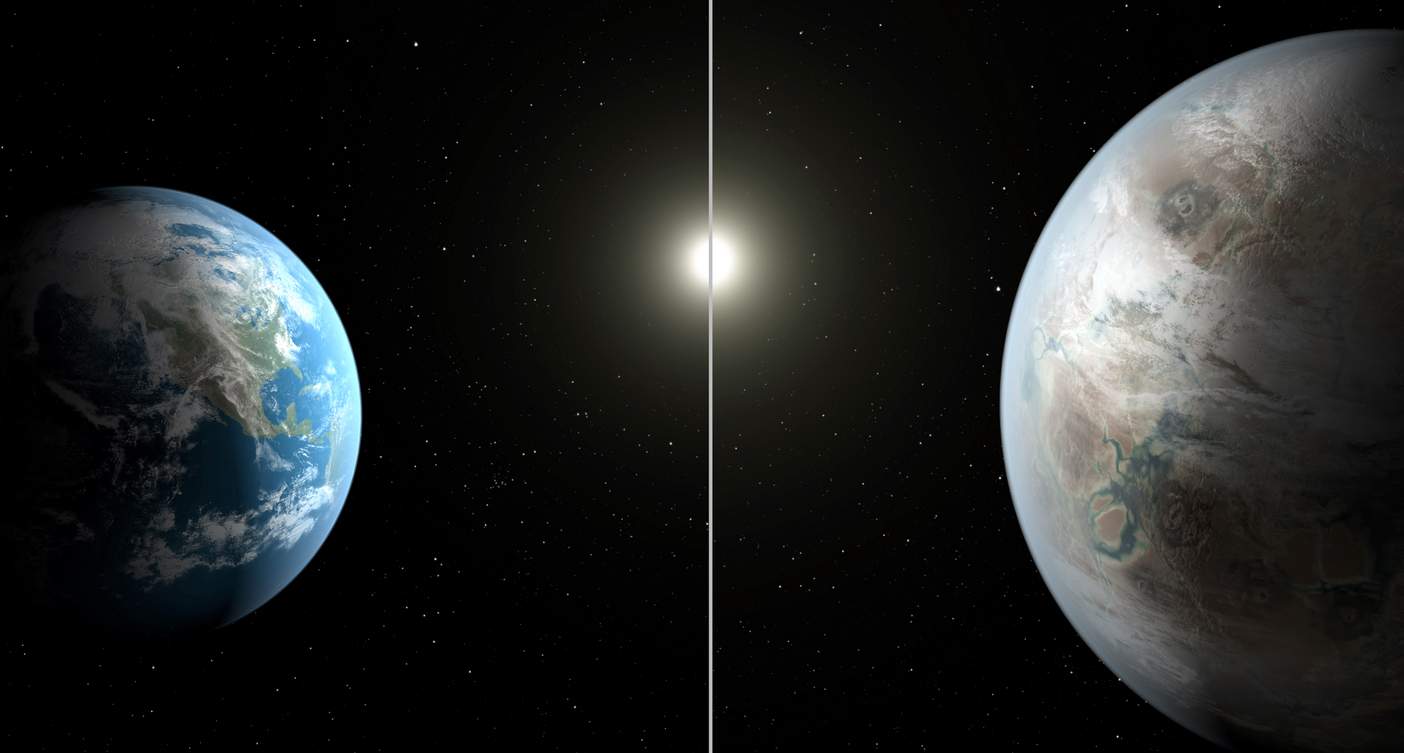
This artist’s concept compares Earth (left) to the new planet, called Kepler-452b, which is about 60 percent larger in diameter (credits: NASA/JPL-Caltech/T. Pyle)
NASA’s Kepler mission has discovered the first near-Earth-size planet in the “habitable zone” around a Sun-like star. This discovery joins 11 other new small habitable zone candidate planets, marking another milestone in the journey to find another “Earth.”
The newly discovered Kepler-452b, located 1,400 light-years away in the constellation Cygnus, is the smallest planet to date discovered orbiting in the habitable zone — the area around a star where liquid water could pool on the surface of an orbiting planet — of a G2-type star, like our sun. The confirmation of Kepler-452b brings the total number of confirmed planets to 1,030.
“It’s awe-inspiring to consider that this planet has spent 6 billion years in the habitable zone of its star; longer than Earth,” said Jon Jenkins, Kepler data analysis lead at NASA’s Ames Research Center, who led the team that discovered Kepler-452b. ” That’s substantial opportunity for life to arise, should all the necessary ingredients and conditions for life exist on this planet.”