New handheld miniature microscope could ID cancer cells in doctor’s offices and operating rooms
January 25, 2016
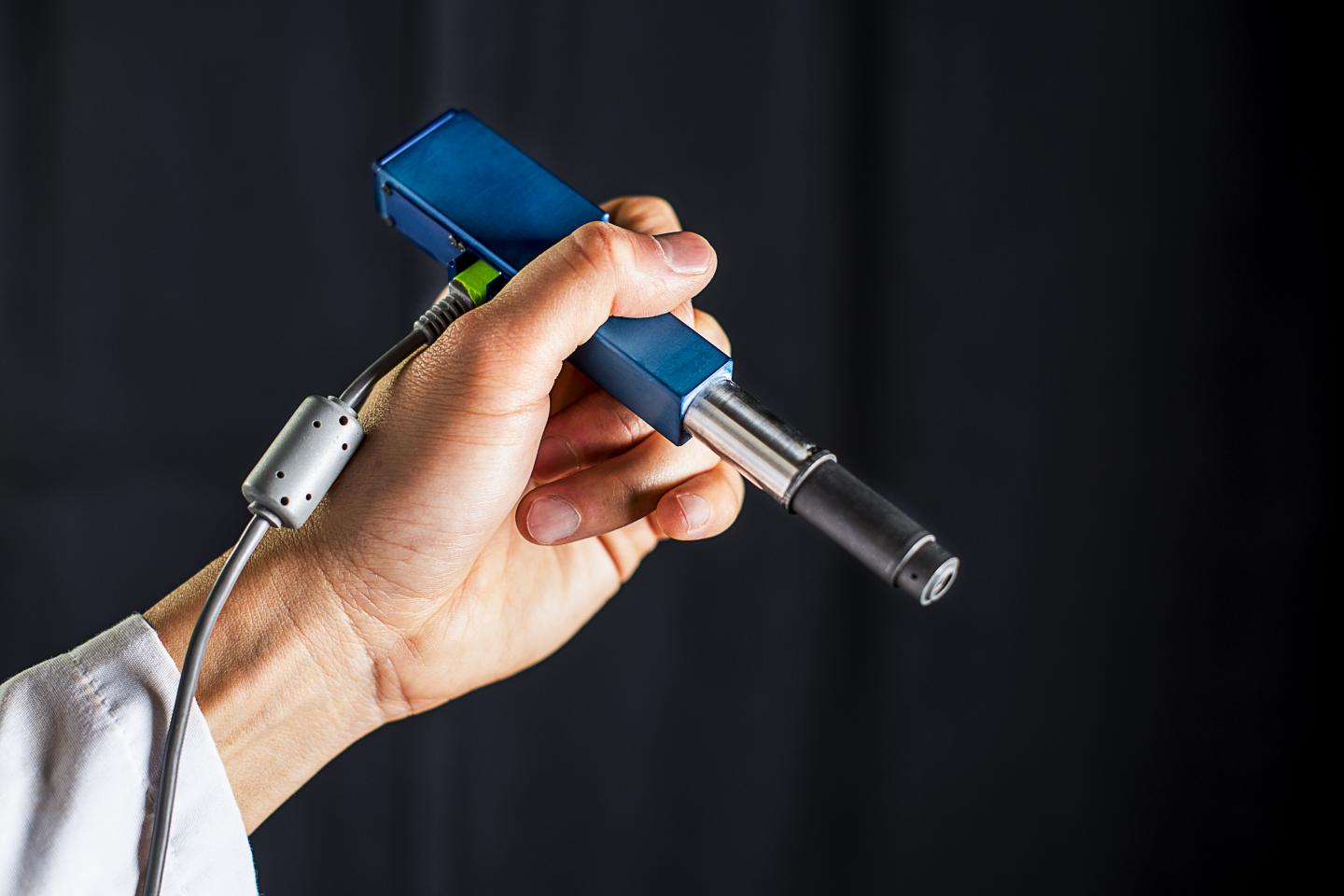
University of Washington mechanical engineers and collaborators have developed a handheld microscope to help doctors and dentists distinguish between healthy and cancerous cells in an office setting or operating room. (credit: Dennis Wise/University of Washington)
A miniature handheld microscope being developed by University of Washington mechanical engineers could allow neurosurgeons to differentiate cancerous from normal brain tissue at cellular level in real time in the operating room and determine where to stop cutting.
The new technology is intended to solve a critical problem in brain surgery: to definitively distinguish between cancerous and normal brain cells, during an operation, neurosurgeons would have stop the operation and send tissue samples to a pathology lab — where they are typically frozen, sliced, stained, mounted on slides and investigated under a bulky microscope.
Developed in collaboration with Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, Stanford University and the Barrow Neurological Institute, the new microscope is outlined in an open-access paper published in January in the journal Biomedical Optics Express.
“Surgeons don’t have a very good way of knowing when they’re done cutting out a tumor,” said senior author Jonathan Liu, UW assistant professor of mechanical engineering. “They’re using their sense of sight, their sense of touch, and pre-operative images of the brain — and oftentimes it’s pretty subjective. “Being able to zoom and see at the cellular level during the surgery would really help them to accurately differentiate between tumor and normal tissues and improve patient outcomes.”
The handheld microscope, roughly the size of a pen, combines technologies in a novel way to deliver high-quality images at faster speeds than existing devices. Researchers expect to begin testing it as a cancer-screening tool in clinical settings next year.
It also has other uses in medicine and dentistry. For instance, dentists who find a suspicious-looking lesion in a patient’s mouth often wind up cutting it out and sending it to a lab to be biopsied for oral cancer. Most come back benign.
That process subjects patients to an invasive procedure and overburdens pathology labs. A miniature microscope with high enough resolution to detect changes at a cellular level could be used in dental or dermatological clinics to better assess which lesions or moles are normal and which ones need to be biopsied.
Key technologies: dual-axis confocal microscopy and line scanning
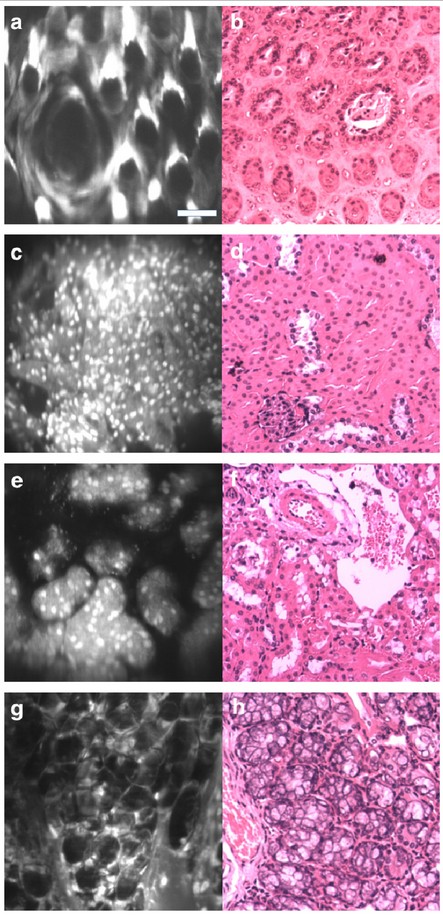
The real-time microscope images (left) illuminate details in mouse tissues similar to the images (right) produced during an expensive, multi-day process at a clinical pathology lab. (credit: University of Washington)
“The microscope technologies that have been developed over the last couple of decades are expensive and still pretty large, about the size of a hair dryer or a small dental x-ray machine,” said co-author Milind Rajadhyaksha, associate faculty member in the dermatology service at the Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York City. “So there’s a need for creating much more miniaturized microscopes.”
Making microscopes smaller, however, usually requires sacrificing some aspect of image quality or performance such as resolution, field of view, depth, imaging contrast or processing speed.
“We feel like this device does one of the best jobs ever — compared to existing commercial devices and previous research devices — of balancing all those tradeoffs,” said Liu.
The miniature microscope uses an innovative approach called “dual-axis confocal microscopy” to illuminate and more clearly see through opaque tissue. It can capture details up to a half millimeter beneath the tissue surface, where some types of cancerous cells originate.
In the video below, for instance, researchers produced images of fluorescent blood vessels in a mouse ear at various depths ranging from 0.075 to 0.125 millimeters deep.
“Trying to see beneath the surface of tissue is like trying to drive in a thick fog with your high beams on – you really can’t see much in front of you,” Liu said. “But there are tricks we can play to see more deeply into the fog, like a fog light that illuminates from a different angle and reduces the glare.”
The microscope also employs a technique called line scanning to speed up the image-collection process. It uses micro-electrical-mechanical (MEMS) mirrors to direct an optical beam that scans the tissue, line by line, and quickly builds an image.
Imaging speed is particularly important for a handheld device, which has to contend with motion jitter from the human using it. If the imaging rate is too slow, the images will be blurry.
In the paper, the researchers demonstrate that the miniature microscope has sufficient resolution to see subcellular details. Images taken of mouse tissues compare well with those produced from a multi-day process at a clinical pathology lab — the gold standard for identifying cancerous cells in tissues.
The researchers hope that after testing the microscope’s performance as a cancer-screening tool, it can be introduced into surgeries or other clinical procedures within the next 2 to 4 years.
“For brain tumor surgery, there are often cells left behind that are invisible to the neurosurgeon. This device will really be the first to let you identify these cells during the operation and determine exactly how much further you can reduce this residual,” said project collaborator Nader Sanai, professor of neurosurgery at the Barrow Neurological Institute in Phoenix. “That’s not possible to do today.”
The research was funded by the National Institutes of Health through its National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research and National Cancer Institute.
University of Washington | Miniature dual-axis confocal microscope imaging
Abstract of Miniature in vivo MEMS-based line-scanned dual-axis confocal microscope for point-of-care pathology
There is a need for miniature optical-sectioning microscopes to enable in vivointerrogation of tissues as a real-time and noninvasive alternative to gold-standard histopathology. Such devices could have a transformative impact for the early detection of cancer as well as for guiding tumor-resection procedures. Miniature confocal microscopes have been developed by various researchers and corporations to enable optical sectioning of highly scattering tissues, all of which have necessitated various trade-offs in size, speed, depth selectivity, field of view, resolution, image contrast, and sensitivity. In this study, a miniature line-scanned (LS) dual-axis confocal (DAC) microscope, with a 12-mm diameter distal tip, has been developed for clinical point-of-care pathology. The dual-axis architecture has demonstrated an advantage over the conventional single-axis confocal configuration for reducing background noise from out-of-focus and multiply scattered light. The use of line scanning enables fast frame rates (16 frames/sec is demonstrated here, but faster rates are possible), which mitigates motion artifacts of a hand-held device during clinical use. We have developed a method to actively align the illumination and collection beams in a DAC microscope through the use of a pair of rotatable alignment mirrors. Incorporation of a custom objective lens, with a small form factor for in vivo clinical use, enables our device to achieve an optical-sectioning thickness and lateral resolution of 2.0 and 1.1 microns respectively. Validation measurements with reflective targets, as well as in vivo and ex vivo images of tissues, demonstrate the clinical potential of this high-speed optical-sectioning microscopy device.