Scientists develop universal DNA reader to advance faster, cheaper sequencing efforts
February 12, 2010 | Source: Physorg.com
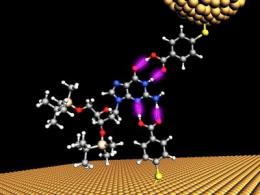
As a single chemical base of DNA (blue atoms) passes through a 2.5nm gap between two gold electrodes, it momentarily sticks to the electrodes (purple bonds) and a small increase in the current is detected, with a unique signature for each of the four DNA bases (Biodesign Institute at Arizona State University)